The thesis aims to restore the relationship between the Villa del Casale in Piazza Armerina, a UNESCO site, and the Gela river, which is identified as a secondary attraction of the entire context; to welcome, within a new access system, the areas highlighted during the excavation campaigns of the last decade, to the south of the Villa and to place them under an adequate system of coverings that protect them and make them accessible.
A secondary target is also to reduce the negative landscape impact of the infrastructures built in the last decade to the north of the Villa and to offer a new solution to the allocation of additional services, the result produce new opportunities for artistic, naturalistic and sporting attractions.

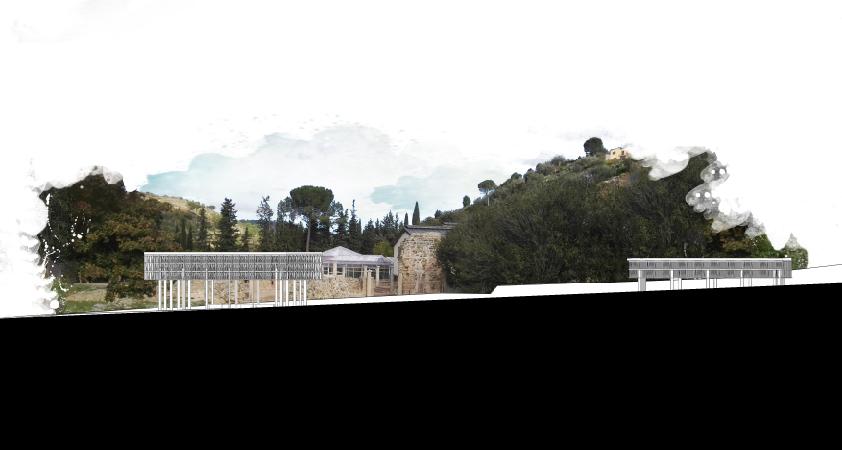
The previous roofing systems designed by Franco Minissi and, subsequently, from Guido Meli they gave different answers to the volumetric questions on the elements that made up the archaeological remains of the villa: a lacking wall structure and extensive mosaic floors in every room. This led to privileging the flooring at the expense of the ridges walls that have undergone questionable additions on various floors. The situation of the new archaeological areas, however, is more varied: the archaeological attention to the various moments of frequentation of the site has allowed to preserve the stratigraphy or to highlight particular and various examples of capital reuse in the wall structures. The elevations tell the story of the factory and of the valley itself. Conversely, the floorings are fragmented and circumscribed only to certain areas of the spa building. It is therefore chosen to differentiate the approach compared to previous hedges. This allows to mark the relationship between the two systems without highlighting each other, basing them on different principles.

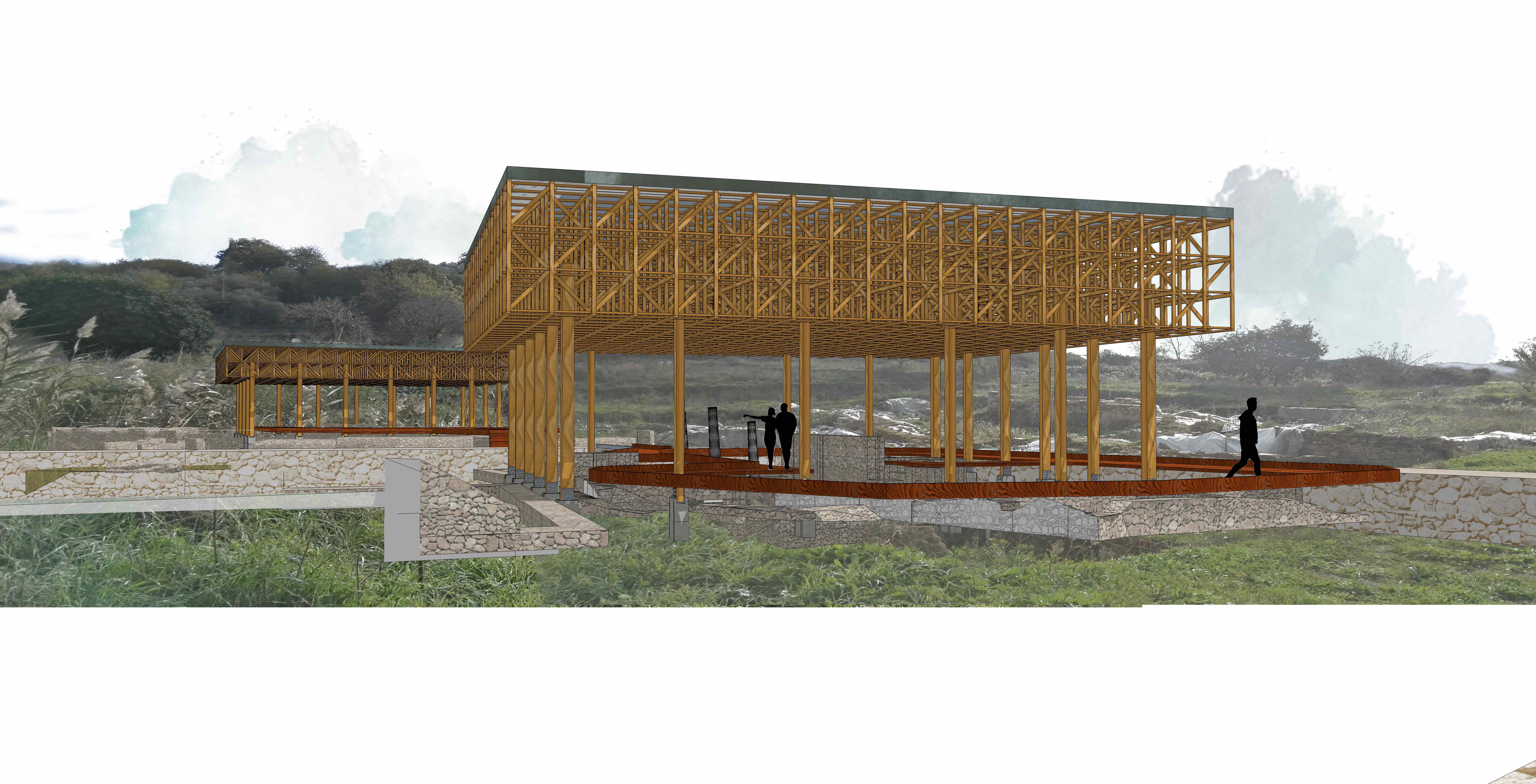
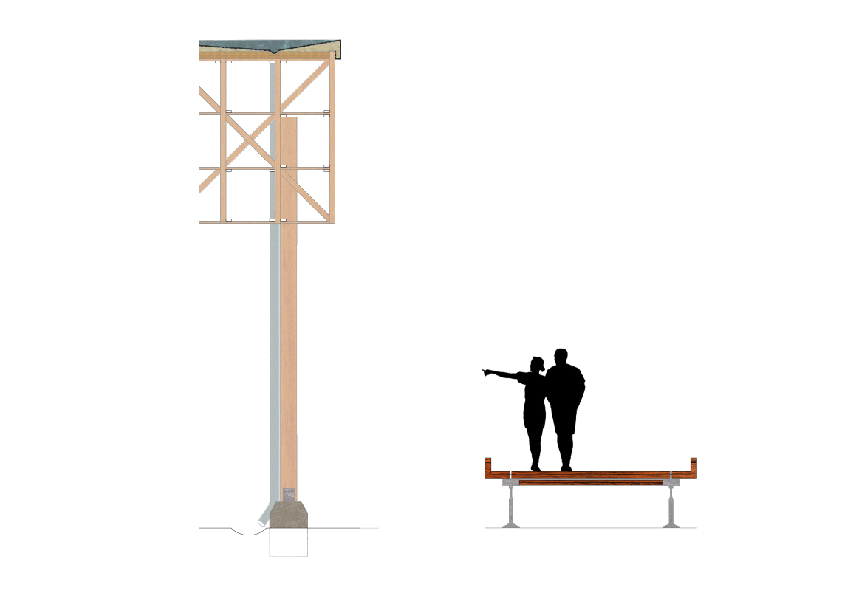
La struttura dei padiglioni si rapporta con la copertura della villa del Casale solamente tramite l'uso del rame zincato di copertura. Il padiglione copre il sito con una struttura aperta ai lati che permette l’areazione pur proteggendo il sito dalla pioggia e dal sole. I mosaici subiranno solo un normale intervento sulle superfici come la bordatura e alcuni risarcimenti localizzati delle lacune, strettamente necessari alla conservazione. I percorsi all’interno degli ambienti nel nuovo scavo sono sopraelevati e in legno, per differenziare il materiale con il percorso che porta alla villa. The structure has concrete bases of 40x40 cm and 100 cm deep, necessary given the presence of a sandy soil. The 30x30 cm lamellar wooden pillars rest on the concrete base. The structure of the roof is composed of a network of reticular beams in lamellar wood. The only apparently complex framework is very light and compact. The pillars are connected to the reticular structure in different points, which are made up of steel hooks and plates. Between the reticular beams and the galvanized copper covering an insulating material is interposed allowing the structure not to heat up and not to affect the conservation of the mosaics.
The Board: